In recent years, the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste projects in cement kilns has shown explosive growth, and the market prospects are very broad, but the industrial development is still in its infancy.
At present, there are five main problems in the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kilns in China: project direction, project design, industrial know-how, policy and operation: (1) project direction problem Some enterprises operate cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kilns only for the purpose of cementing non-stop production, and the quality of disposal is difficult to guarantee; (2) project design problem is not detailed enough for the investigation of hazardous waste market to cement production. The scale of application for business license is too large; (3) the technology of cement production process control needs to be improved in the process of synergistic disposal of industrial proprietary technical problems, and the equipment of waste conveying into kiln and pretreatment needs to be upgraded; (4) in the mode of “pretreatment + cement kiln” operation, the product quality standard of pretreatment Center is not clear, resulting in It is difficult to implement it in practice; (5) The operation problem is extensive management of hazardous waste disposal process line with the thinking of cement production, and it is difficult to balance the output of cement production and the quantity of hazardous waste disposal.
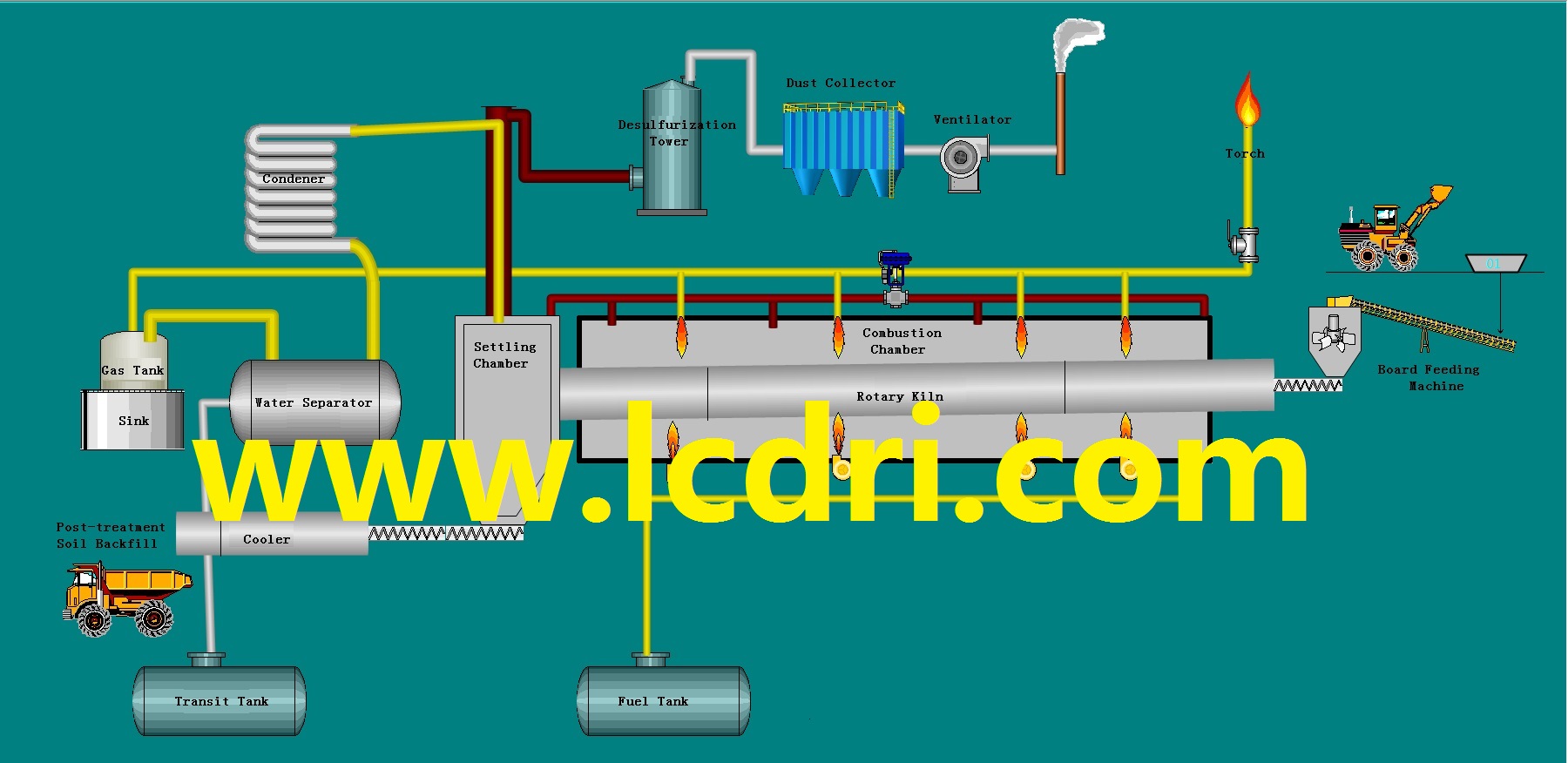
Cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kiln is a waste disposal method which can decompose, degrade, eliminate, inert and stabilize the toxic characteristics of hazardous waste through high temperature incineration and sintering of cement clinker minerals, and reuse the useful components at the same time. The ability of synergistic disposal of hazardous wastes is related to the process condition of cement kiln, raw material condition and waste characteristics. High disposal temperature, strong stability, long residence time, large incineration space, large scale of treatment, environmental protection and safety, no residue is an important technical advantage of collaborative treatment of hazardous wastes.
Collaborative disposal of many wastes in cement kilns is prohibited, including radioactive wastes, contagious, explosive and reactive wastes, undisassembled waste batteries, waste household appliances and electronic products, mercury-containing thermometers, sphygmomanometers, fluorescent lamps and switches, chromium slag produced during the production of chromium salts by calcium roasting process, asbestos wastes, unknown characteristics and unidentified ones. Solid waste, etc.
The key points of the process for the co-disposal of hazardous wastes in cement kiln are as follows: (1) the burnable materials should be avoided from contacting directly with the materials in the anaerobic state; (2) the oxygen content in the decomposition furnace is related to the discharge; (3) the process accidents can be reduced by setting the decomposition furnace temperature reasonably; (4) the pulverized coal should be fully burned, otherwise the cement performance will be affected.
Through the control of detection, calculation and adding speed, the content of “unnecessary” elements in clinker can be guaranteed to be within the capacity. Because of the physicochemical characteristics of hazardous waste, the waste with high volatility, flammability, explosiveness and strong cohesion should be guaranteed to enter the kiln safely. It is necessary to ensure that no secondary pollution occurs during storage, transshipment and tail gas discharge.
There are several points about the future development of the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kiln: (1) The cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kiln is a direction of industrial development, and will eventually change from harmless to resource-based. With the improvement of disposal capacity, the market price of hazardous waste disposal will fall back; (2) With the development of industry and the improvement of policy, the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kiln will return to the essence of hazardous waste disposal, and will no longer be the talisman of “staggered peak production”; (3) the regional government should formulate a plan for the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste in cement kiln to avoid regional surplus; (4) the cooperative disposal of hazardous waste suitable for China’s national conditions of high water. Lack of complete sets of pretreatment and disposal equipment with high automation and quality will bring opportunities for development in the field of equipment; (5) Standards for disposal of hazardous waste in cement kilns will continue to be improved, and existing policies will be refined and landed.
Luoyang Building Material Architectural Design and Research Institute is committed to the innovation and development of technology and equipment in building materials and construction industry. It has Grade A design and Research Institute which integrates scientific research and development, design, general contracting, supervision, technical consultation and technical service of building materials and construction engineering. At present, more than 60 new dry-process cement clinker production lines of various scales (300-8000 tons per day), more than 10 low-temperature waste heat power generation projects supporting cement clinker production lines, more than 20 cement grinding station projects and dozens of other industrial and civil construction projects have been completed.