The water demand of cement has already attracted the attention of cement users. Especially in the areas where commercial concrete is developed, more and more users are placing higher and higher requirements on the water demand of cement. Concrete producers are hoping to choose cements that require less water, which affects the competitiveness and price of cement companies’ products, and affects the costs and benefits of cement producers.
There are many factors affecting the water demand of cement, and the restriction of the grinding process is one of them. In other words, the cement produced by different grinding processes has different water requirements. This is understood by everyone. However, precisely because everyone understands this, if we want to improve the efficiency of the grinding system, no matter what more advanced grinding process we use, we must consider whether the water demand of the cement is appropriate. Otherwise, we must strike a balance between grinding efficiency, grinding costs and water demand.
Cement water demand
Cement standard consistency water demand (hereinafter referred to as cement water demand), the accurate characteristic parameter should be the standard consistency water consumption of concrete, which refers to the amount of mixing water required to make the cement slurry reach a certain degree of plasticity and fluidity. It is used for cement. An important indicator of performance.
The water demand of cement directly affects the water-cement ratio of concrete, which in turn affects the strength, corrosion resistance, frost resistance and durability of concrete, affects the amount of cement used in concrete production and the amount of admixture, which affects the cost and benefit of users.
The greater the standard consistency of cement, the greater the amount of water used to reach the standard consistency of the cement paste, the amount of water used to reach the specified degree of fluidity of the cement mortar, and the greater the amount of water used to achieve a certain slump in the cement concrete. The greater the water-cement ratio of mortar and concrete, the more intergranular voids and the smaller the compactness, which deteriorates the construction performance, mechanical properties and durability of cement and concrete.
Intuitively, the formulation of concrete has three basic parameters: water-cement ratio, water consumption, and sanding rate.
Two of the three parameters relate to water, which shows the importance of the water consumption problem of cement standard consistency in concrete. The strength of concrete is inversely proportional to the amount of water used. In order to increase the strength of concrete, it is necessary to reduce its water consumption.
In theory, to maintain the strength of the concrete, when the water consumption of the concrete changes, the water-cement ratio should be kept constant, and the amount of cement should be adjusted accordingly, but this is difficult to achieve in actual production operations.
Due to the limitations of experimental conditions and process equipment, it is difficult for ready-mixed concrete plants to adjust the amount of cement according to the change in water demand of each batch of cement. In most cases, the amount of cement and the amount of sand and other materials are kept constant, and the amount of water is adjusted according to the slump value. Thus, the actual water-cement ratio of the concrete will vary with the change in the water demand of the cement, which in turn affects the strength of the concrete. Therefore, in order to stabilize the strength of the concrete, it is necessary to stabilize the standard consistency water consumption of the cement.
Reducing the standard consistency of cement requires water. It is of great significance to the concrete industry to reduce the single cubic water consumption of concrete, thereby increasing its strength, reducing the amount of cement, and saving concrete production costs.
Main factors affecting cement water demand
The first is the influence of cement specific surface area, particle gradation, and particle shape.
The second is the influence of the type and amount of cement mixed materials.
The third is the effect of gypsum on the water demand of cement.
The fourth is the effect of clinker on the water demand of cement.
The fifth is the impact of the grinding process on water demand.
1. The influence of specific surface area, particle gradation and particle shape of cement
Relevant research shows that if the cement specific surface area is 300~400m2/kg, if the particle size distribution slope n of the cement and the clinker reactivity are unchanged, the water content of the standard consistency will increase by 100m2/kg. 6%. The German Cement Research Institute has carried out tests on the influence of specific surface area, particle gradation and particle shape on the water demand of cement for cements of different strength grades. The correlation between cement water demand and specific surface area is strong, with the increase of specific surface area. The water demand has increased significantly.
Tests have shown that cement particle size has a large impact on the water demand of cement. Good cement particle grading reduces the inter-particle gap, which can reduce the filling water, thereby reducing the water demand of the cement. Therefore, in our improvement of the grinding system in recent years, it is felt that both the powder separator and the entire grinding system, as long as the efficiency of the powder selection is increased, the water demand is increased.
The narrower the distribution of cement particles, the larger the porosity of the stack, the greater the water demand
For the strength of cement, the particles with 3μm~32μm play a leading role, especially the particles of 16μm~24μm are very important for cement performance, the more the content is better; the fine particles of <3μm are easy to agglomerate, especially <1μm (mainly refers to Clinker) granules hydrate quickly after adding water, which has a great influence on the water demand of cement, but has little effect on concrete strength, and it is easy to cause concrete cracking, affecting the durability of concrete and affecting the adaptability of cement and admixture. ;>65μm particles hydrated very slowly, contributing little to the 28d strength.
Tests have shown that the shape of the cement particles also has a large impact on the water demand of the cement. The effect of the sphericity of cement particles on their water demand is shown in the table below. The higher the sphericity of the cement particles, the:
(1) The smaller the surface area of the particles, the smaller the surface area required for lubrication → the smaller the water demand of the cement;
(2) The smaller the internal friction between the particles, the smaller the surface water film thickness required for the flow → the smaller the cement water requirement;
(3) The smaller the voids in which the particles are deposited, the smaller the required filling water is. The smaller the cement water requirement is.
Effect of sphericity of cement particles on its water demand
| project |
Specific surface area |
Particle sphericity |
Cement water demand |
| unit |
M2/kg |
% |
% |
| Sample A |
345 |
47 |
30.40 |
| Sample B |
348 |
73 |
27.30 |
When the specific surface area is basically the same, when the sphericity of the cement particles is increased from 47% to 73%, the cement water demand drops from 30.4% to 27.3%.
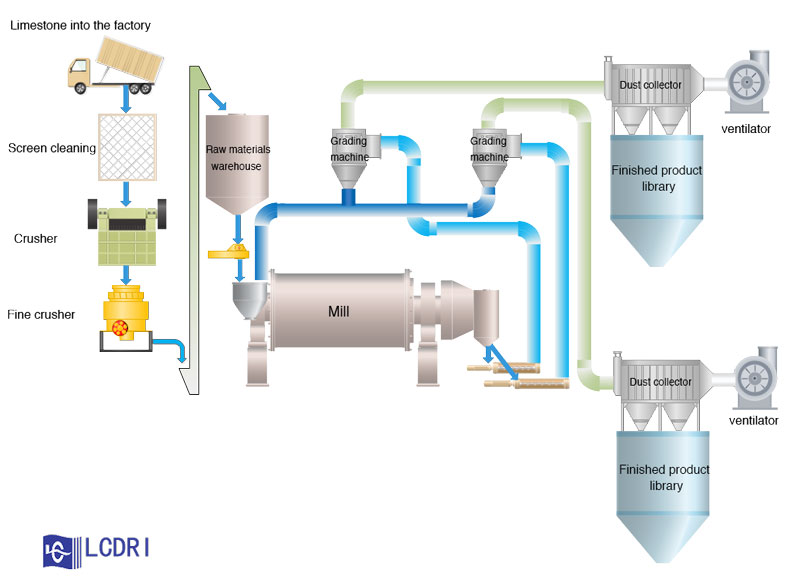
2. Effect of grinding process on water demand
Although there are more than one factor affecting the water demand of cement, the grinding process factor is optional during construction and is not easily changed once selected. Because of its subsequent production and the impact of water demand on the balance of other factors, it is a price. Therefore, when initially selecting the grinding process, the factor of water demand should be considered.
In the case of the same raw materials, the cement produced by different grinding processes differs in water demand due to the difference in particle gradation and particle shape. In terms of the existing common grinding process, the order of the cement water demand is roughly as follows: semi-finished grinding of the roller press>double closed circuit combined grinding>single closed circuit combined grinding>closed grinding>opening grinding.
Compared with the ordinary circle flow grinding cement, the open flow grinding cement particles have a wide distribution, the roundness coefficient is large, and the cement requires less water; and the cement produced by the roller press and the vertical mill includes the final grinding and the semi-final grinding. Combined grinding, due to the narrow distribution of cement particles and the low spherical shape of the particles, the cement requires relatively large water.
At present, the cement grinding of most cement enterprises adopts the double closed circuit combined grinding system of “roller press + ball mill”. The grinding efficiency is indeed high, and the power consumption is indeed reduced. However, due to the excessive concentration of cement particles, the water demand is still high. This is necessary to increase the amount of concrete water reducing agent used and increase the cost of the concrete mixing plant. In the case of oversupply in the cement market, the mixing station does not buy much, and ultimately it will affect the sales volume and selling price of the company.
In addition to the influence of the roller press on the shape of the cement particles, in general, the closed-circuit grinding system, especially the closed-circuit system using the high-efficiency classifier, has a narrow particle size distribution, the particle size uniformity coefficient is 1.0~1.2, and the water demand is required. Up to 26.0% to 28.0%. The cement of the open grinding system has a wide particle size distribution range, the uniformity coefficient is 0.9~1.0, and the water demand of cement is about 24%.
Semi-final grinding and cement water demand
The so-called semi-final grinding, precisely in the pre-grinding stage of the grinding system, select a part of the semi-finished products that have passed the fineness in advance, and directly add them to the finished product, so that the products with fineness have passed, leave early. The grinding system no longer accepts subsequent grinding, which improves the powder selection efficiency of the entire grinding system (not only the classifier), reduces the phenomenon of over-grinding, reduces the waste of grinding energy, and improves the grinding efficiency of the system. The semi-finish grinding process is actually an optimization of the original grinding process by using the closed circuit process of the powder selecting equipment. Depending on the pre-grinding equipment selected, there are many specific forms, but due to the improved efficiency of the system, the grinding efficiency is certain. At present, the pre-grinding equipment used in the semi-finishing grinding process is mainly a roller press, and other vertical grinding, wind-selecting grinding, ball grinding and the like.
Regarding the problem of cement water demand in the semi-finishing grinding process, several semi-finish grinding processes are not the same. It depends on what equipment is used in the pre-grinding stage, and the semi-finished products that have been qualified in advance are selected in advance. What is the difference between some finished products, resulting in changes in the content of fine powder, particle gradation and particle shape in the final product.
The increase in the content of the fine powder, the narrowing of the particle gradation, and the non-spherication of the particle shape all lead to an increase in the water demand of the cement. For example, the early two-ball mill grinding process (the first one is closed) is the earliest semi-finish grinding, which not only improves the grinding efficiency, but also reduces the phenomenon of over-grinding and reduces the micro-powder content of cement. Reduce the water demand of cement; for example, in recent years, cement mills that have been modified from unloading and drying mills in raw materials should be compact semi-finished grinding, although the grinding efficiency is not reduced, but due to the particle size of the cement. With a narrower distribution, the water demand of cement has increased, so it has not been promoted. Nowadays, most of them say that the semi-final grinding actually refers to the semi-final grinding of the roller press, which is to add part of the unshaped fine powder collected by the closed circuit system of the roller press to the finished cement product.
The water requirement for the semi-finished cement of the roller press depends on the fine powder content (hydration speed) of the cement, the particle grading (bulk density), and the particle shape of the cement (flow internal friction). The reduction of the content of the micropowder and the widening of the gradation can reduce the water demand of the cement; however, the dissimilation of the particle shape (non-spherical) can increase the water demand of the cement. It has been proved that the water demand of the cement of the semi-finish grinding system of the roller press is generally increased. As for the increase in water demand, it is related to the characteristics and fineness of the raw material entering the roller press, that is, the degree of dissimilation of the particle shape of the roller press.
Because of the addition of a classifier between the V-selector and the cyclone, it ensures that the materials collected by the cyclone dust collector all meet the requirements of the finished cement product. This improvement can increase the capacity of the grinding system and reduce the power consumption of the grinding, but at the same time reduce the expansion capability of the finished cement particle grading. Moreover, it is certain that this part of the material is mainly a fine powder of a roller press which is not shaped by a ball mill, and the sphericity of the particles is inferior.
The bulk density and fluidity that affect the water demand of the cement are related to the particle size of the cement, and also related to the particle shape of the cement. The roundness coefficient (the circumference of the circle equal to the projected area of the particle and the actual circumference of the projected area of the particle) The higher the ratio, the smaller the internal friction of the cement particles, the smaller the surface area of contact with water, and the smaller the standard consistency water requirement.
The roller press is crushed once by the material bed, and the efficiency is high, but the sphericity is not good. The ball mill is a multi-impact grinding machine with low efficiency and high sphericity, which is the main reason why the roller press can not drop the ball mill. But this does not mean that the roller press semi-final grinding system is useless, but it can be said to be a result of refined management. Although the semi-finish grinding of the roller press has the disadvantage of high water demand of cement, it is indeed effective for improving the output of the grinding system and reducing the power consumption. Any improvement in performance is accompanied by a targeted improvement and a decline in adaptability. As long as we can use it to avoid it, the semi-finishing of the roller press can still make a difference.
The conditions for the semi-final grinding of the roller press are: the materials with small particle shape of the roller press (such as fine fly ash), the market and users who are not sensitive to the water demand of the cement, and most of the low-grade cement. For the cement open-circuit grinding system, the cement with relatively low surface area control, the clinker with low water demand, and the cement with fine slag powder.
The factors that are not suitable for the semi-final grinding of roller presses are: for the market and users with demanding water requirements for cement, for most high-grade cements, for cement closed-circuit grinding systems, for cements with relatively high specific surface area control, Clinker with high water content, for relatively poor limestone mines, for raw materials with relatively high alkali content.
In fact, the above conditions are not static, and sometimes they are not adapted. We can design or transform the process of “half-finish grinding” and “combined grinding” to switch on demand. When the conditions are met, the capacity will be maximized, the power consumption will be minimized, and the joint grinding will be switched when the conditions are not met. If there is some potential, the adjustment of the semi-finished powder separator can be appropriately reduced. The final amount.
Vertical mill grinding and cement water demand
Although the vertical grinding final grinding system has many advantages such as high grinding and drying efficiency, good adaptability to the grinding materials, simple process flow, compact space arrangement and low maintenance cost, cement grinding is the guarantee of the quality of cement products. At the last level, everyone is still worried about the performance of vertical mill cement, especially for the high water demand of cement. The process technology of this cement grinding is still limited in China.
In fact, the cement vertical grinding final grinding products can be compared with the ball mill, which can meet various engineering needs. The selection rate of the cement vertical grinding final grinding process has shown an increasing trend year by year.
The selection rate of cement vertical grinding final grinding process is increasing year by year.
| area |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
| World (excluding China) |
15% |
45% |
70% |
| China Mainland |
0.0% |
0.2% |
0.8% |
According to relevant information, from 2005 to 2008, about 360 new cement production lines in the world (except mainland China), the annual cement production capacity reached 440 million tons, and more than 600 sets of cement grinding equipment were used. The selection rate of vertical mill increased from 45% in 2005 to 61% in 2008, while the selection rate of cement ball mill decreased from 50% to 27%.
With the gradual increase of the final grinding process, the technology is further improved and matured. The problem of cement particle shape and gradation, fineness control and water demand, which are worried about the cement performance, is now also It is not a problem.
Through the combination of the grinding disc and the grinding roller grinding curve, the improvement of the performance of the grinding machine, the height of the retaining ring, the adjustment of the rotating speed and pressure of the grinding disc, the optimization of the shape and grading of the cement particles is realized. In terms of system operation, it is also possible to optimize the performance of the cement by increasing the temperature inside the vertical mill and exerting an influence on the dehydration of the gypsum. By comprehensively using these control methods, the performance of vertical mill cement can be controlled in a wide range, so that the particle ratio ratio is even more reasonable than ball mill cement.
Studies on different grinding systems have shown that the highest water requirement is the cement of the closed-circuit combined grinding system, not the cement of the vertical grinding system.
Grinding and water demand separately
The separate grinding of cement is a grinding technology that saves electricity (reduced electricity consumption) and reduces carbon consumption (reduced carbon emissions). In addition, it optimizes the performance of the cement and meets the different requirements of the user for cement performance (such as the water demand of cement). How to achieve the optimal particle distribution of various components such as clinker in cement under the condition that the wearability of each component is very different, it should be said that grinding is the best choice at present.
Grinding separately can set and realize the optimal particle size distribution of each component of cement to achieve the maximum utilization of clinker activity and full digging of the active potential of the mixture. At present, cement mills in advanced countries have rarely used mixed grinding processes.
One of the advantages of separate grinding is that it can easily adjust the particle gradation. The fine powder in the cement not only reduces the water demand due to its ability to increase the fluidity of the cement, but also increases the water demand by speeding up the hydration speed. The grinding has created the conditions for the balance of our balance. Further analysis will reveal that the main factors affecting the hydration rate of cement are clinker components. As long as we reduce the fine powder of clinker and increase the fine powder of other inert mixed materials (such as limestone), we can satisfy the contradiction between the two parties to reduce the water demand of cement. Claim.
Germany’s research shows that in the mixed slag cement, the characteristic particle size of the clinker is smaller than that of cement. The characteristic particle size of the slag is larger than that of cement. The characteristic particle size of gypsum is much smaller than that of cement. In the separately ground cement, When the material composition and the specific surface area are the same, the characteristic particle size of the clinker is reduced by 2.0 μm on average, and the characteristic particle size of the slag is reduced by 7.5 μm on average.
The so-called “characteristic particle size” is actually an approximate embodiment of “volume average particle size”. That is to say, in the case of the same specific surface area, the separate grinding can make the clinker and slag finer, and the fine powder is not too much, which is exactly what we expect. The operation of grinding in foreign countries has not stopped. There is a company that supplies cement for the concrete mixing station. In order to meet the various requirements of the mixing station for cement, and to reduce the production cost, nearly 20 targeted ones have been developed. The variety of cement.
The benefits of separate grinding:
1. The particle size distribution of clinker powder is close to the optimal performance RRSB equation, the clinker fine particles affecting the performance of cement and concrete are few, and the clinker coarse particles affecting the hydration rate are also rare;
2. The fineness of the mixed material is significantly thinner than the clinker. After mixing with the clinker powder, the particle size distribution of the cement is close to the Fuller curve, which ensures that the cement has a lower porosity;
3. The clinker powder with different particle size distribution and the mixed material with different particle size distribution can be combined in a certain ratio to realize the particle gradation design of cement and produce the cement with the expected performance;
4. Not only the early strength of the cement is high, but also the late and long-term strength develops well;
5. Hydration heat, especially early hydration heat is low, compatibility with water reducing agent is good, concrete has good workability;
6. It is possible to mix a variety of mixed materials to produce a multi-component combination of cement, thereby exerting performance complementation and superposition effects of different types and different particle distributions to optimize cement performance;
7. It can flexibly organize the production of multi-variety cement, and the process of changing production is quick and convenient, meeting the different needs of customers;
8. Even with the hard-grinding high-fine slag powder, the cement with a specific surface area of 350~420m2/kg has a combined power consumption of only 31~35kWh/t.